Coronary Artery Disease
What is Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)?
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a common type of functional heart disease that occurs when the arteries that supply blood to your heart become narrowed or blocked. Where does this narrowing occur? It happens within the coronary arteries, the vessels responsible for delivering oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle. This narrowing is caused by a buildup of plaque, a substance made up of fat, cholesterol, and other cellular waste products, within the artery walls. This reduces blood flow to the heart muscle.
Are coronary artery disease and atherosclerosis the same thing?
Atherosclerosis is the underlying process that leads to CAD. It involves the accumulation of fatty substances, cholesterol, cellular waste products, and calcium in the artery walls, forming plaques. Over time, these plaques can harden and narrow the arteries, restricting blood flow to the heart.
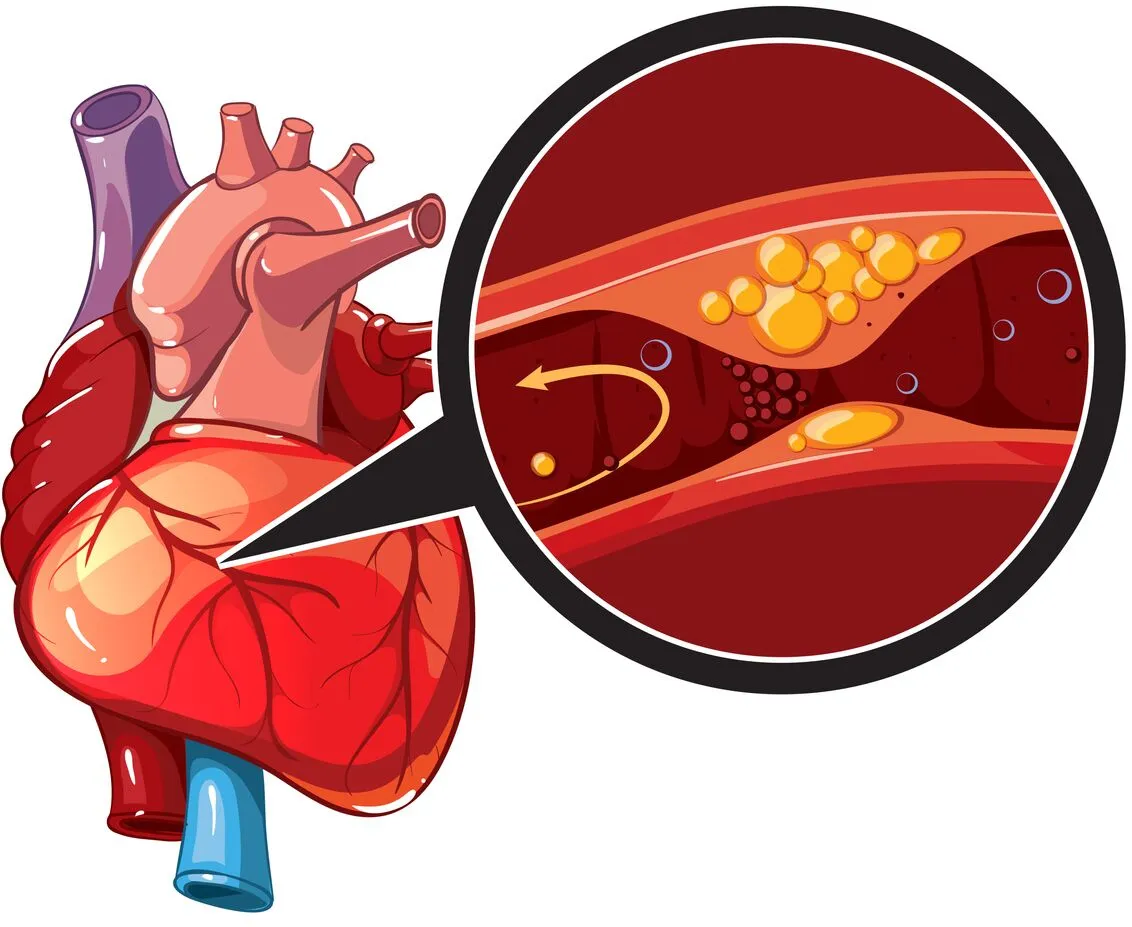
Symptoms of Coronary Artery Disease
When is coronary artery disease diagnosed? Symptoms of CAD can vary depending on the severity of the condition but some common symptoms include:
- Chest pain or discomfort (angina)
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Pain in other parts of the body, such as the arms, neck, or jaw
- Heart palpitations
- Dizziness
Silent Heart Attacks
A significant concern with CAD is the possibility of a “silent heart attack.” This occurs when a heart attack happens without noticeable symptoms. It’s essential to be aware of the risk factors and undergo regular check-ups, especially if you have a family history of heart disease.
Who Does Coronary Artery Disease Affect the Most?
Risk Factors for Coronary Artery Disease
Several factors can increase your risk of developing CAD, including
High blood pressure
Smoking
Obesity
Diagnostic Tests for CAD
How coronary artery disease is diagnosed? Early detection of CAD is crucial for effective disease management. Several diagnostic tests can help identify the presence and severity of the disease
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Can coronary artery disease be detected by ECG? A doctor uses an ECG to investigate: signs of damage to the heart, abnormal heartbeat rhythms, known as arrhythmias, and the effect of electrolyte abnormalities or drugs on the heart’s electrical system.
Stress Test
Evaluates heart function during exercise.
Echocardiogram
Cardiac CT Scan
Coronary Angiography
Uses X-ray imaging to visualize the coronary arteries.
Complications of Coronary Artery Disease
If left untreated, CAD can lead to serious complications, including
Heart Attack
Stable Angina
Unstable Angina
Heart Failure
General FAQs
Coronary artery disease is a primary culprit in the development of heart failure. When the coronary arteries become narrowed due to plaque buildup, the heart muscle receives less oxygen and nutrients. Over time, this reduced blood supply weakens the heart muscle.
Additionally, the constant strain on the heart from working harder to pump blood through narrowed arteries can eventually lead to heart enlargement and weakening. This weakened heart muscle is unable to pump blood efficiently throughout the body, resulting in heart failure. Essentially, CAD progressively damages the heart muscle, impairing its ability to function effectively, ultimately leading to heart failure.
Yes, CAD is a serious condition that can be fatal. It is the leading cause of death worldwide. Sudden cardiac death (SCD) is a catastrophic event where the heart abruptly stops beating. In many cases, it’s caused by fatal heart arrhythmias, often triggered by underlying heart conditions such as coronary artery disease (CAD). While the exact cause of SCD can vary, CAD is a significant risk factor. Early detection and treatment of CAD are crucial in preventing this life-threatening complication.
Prevention and Management of Coronary Artery Disease
Quitting Smoking
Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Regular Exercise
Diet and Weight Management
Stress Management
Managing Blood Pressure and Cholesterol Levels
Regular Check-Ups and Screenings
Medical Procedures
How coronary artery disease is diagnosed? Early detection of CAD is crucial for effective disease management. Several diagnostic tests can help identify the presence and severity of the disease
Angioplasty and Stenting
Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG)
Living with Coronary Artery Disease
Coping with a CAD diagnosis can be challenging, but with proper management, you can lead a fulfilling life. Here are some tips
Support Groups
Stress Management
Regular Check-ups
Emergency Preparedness
Why Choose Coronary Artery Disease Treatment in Dubai?
Expertise
Dr. Mazen brings a wealth of experience and specialized knowledge in diagnosing and treating complex structural heart conditions all the way from the United States to Dubai.
Personalized Care
Advanced Technology
Minimally invasive procedures for optimal outcomes.
Compassionate Care
A supportive and patient-centered approach throughout your treatment journey.
Proven Results
Secure Your Path to Better Heart Health!

